Total cholesterol
Watch our video about Total cholesterol
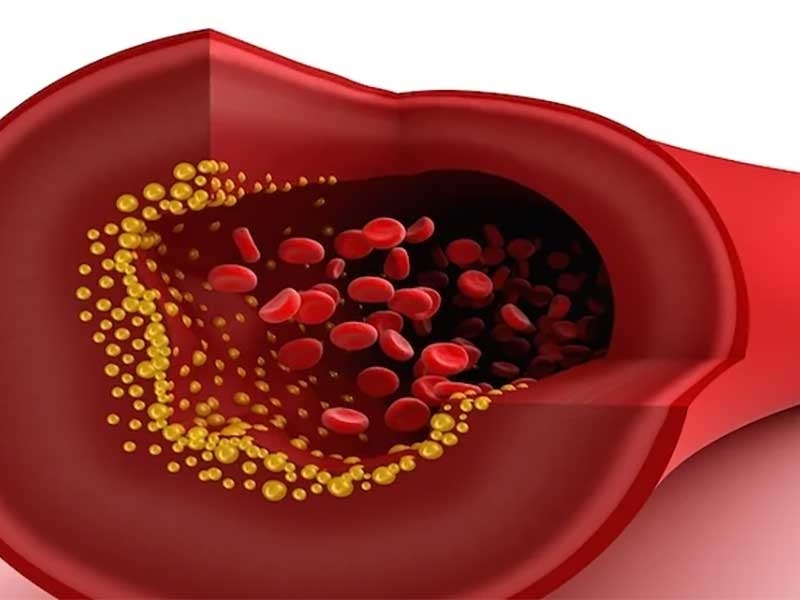
A Total Cholesterol Test is a Blood test that measures the overall amount of cholesterol in your blood. Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance that is essential for building cells and producing hormones, but too much of it can lead to heart disease and other health problems. The test evaluates levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL), high-density lipoprotein (HDL), and triglycerides, all of which contribute to your total cholesterol number. This test is crucial for assessing cardiovascular health and identifying risk factors for conditions like atherosclerosis, heart attacks, and strokes.
During the procedure, a healthcare provider will draw a small sample of blood from a vein, usually from the arm. The blood is then analyzed in a laboratory to determine cholesterol levels. The test is simple, fast, and provides critical insights into your heart health.
Types of Cholesterol Measured in a Total Cholesterol Test
Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) Cholesterol
Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often referred to as “bad cholesterol,” can build up in the walls of your arteries, causing them to narrow and harden. This process, known as atherosclerosis, can restrict blood flow, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Monitoring LDL levels is essential for identifying cardiovascular risks early and implementing lifestyle changes or treatments to lower cholesterol levels.
An LDL test is part of the total cholesterol test and provides specific insights into how much "bad" cholesterol is circulating in your bloodstream. If your LDL levels are high, your doctor may recommend dietary adjustments, exercise, or cholesterol-lowering medications to reduce the risk of heart disease.
High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) Cholesterol
High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, known as “good cholesterol,” helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream and transports it back to the liver, where it can be processed and eliminated from the body. High levels of HDL are associated with a lower risk of heart disease, as they help keep arteries clear of plaque buildup.
During a total cholesterol test, HDL levels are measured alongside LDL to provide a complete picture of your cholesterol balance. If your HDL levels are too low, it may indicate an increased risk of cardiovascular issues, and your healthcare provider may recommend lifestyle changes to boost HDL levels, such as incorporating healthy fats into your diet and exercising regularly.
Advantages of the Total Cholesterol Test
The total cholesterol test provides several benefits:
- Early detection of heart disease risks: By measuring LDL, HDL, and total cholesterol, the test helps identify potential cardiovascular risks before they become serious, allowing for timely intervention.
- Quick and simple: The test requires only a small blood sample, and results are usually available within 24 hours, providing fast insights into your heart health.
- Non-invasive: This test is straightforward and minimally invasive, requiring just a simple blood draw.
The entire process takes just a few minutes, and the results provide essential information that can help guide dietary and lifestyle adjustments to improve your overall health.
Pre- and Post-exam Care
Pre-exam care: In most cases, you will need to fast for 9 to 12 hours before a total cholesterol test, meaning no food or drinks except water. This ensures that the test results are not influenced by any recent meals. It’s also important to inform your healthcare provider about any medications you’re taking, as some can affect cholesterol levels.
Post-exam care: After the blood sample is taken, you can return to your normal activities right away. You may experience slight tenderness or bruising at the site of the blood draw, but this usually resolves within a day. If your cholesterol levels are abnormal, your healthcare provider will discuss next steps, including lifestyle changes or medications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How often should I get a cholesterol test?
It is generally recommended that adults over 20 have their cholesterol checked every 4 to 6 years. Those with risk factors for heart disease, such as a family history or high blood pressure, may need more frequent testing.
2. What do high cholesterol levels mean?
High cholesterol levels, especially high LDL, can increase your risk of heart disease and stroke. If your cholesterol is elevated, your doctor may recommend dietary changes, exercise, and possibly medication to help lower your levels.
3. Can I take my regular medications before the test?
Certain medications can affect cholesterol levels, so it’s important to inform your doctor about all medications and supplements you’re taking. Your healthcare provider will let you know if any adjustments need to be made before the test.
Total Cholesterol Test Services at Clinic Consultation
At Clinic Consultation, we offer comprehensive total cholesterol testing to help you monitor and manage your heart health. Our team of healthcare professionals provides accurate, timely results to help you take control of your cholesterol levels and reduce your risk of heart disease.
Book an appointment today to schedule your total cholesterol test at Clinic Consultation and take a proactive step toward better cardiovascular health.
Click the button below to schedule your appointment online.