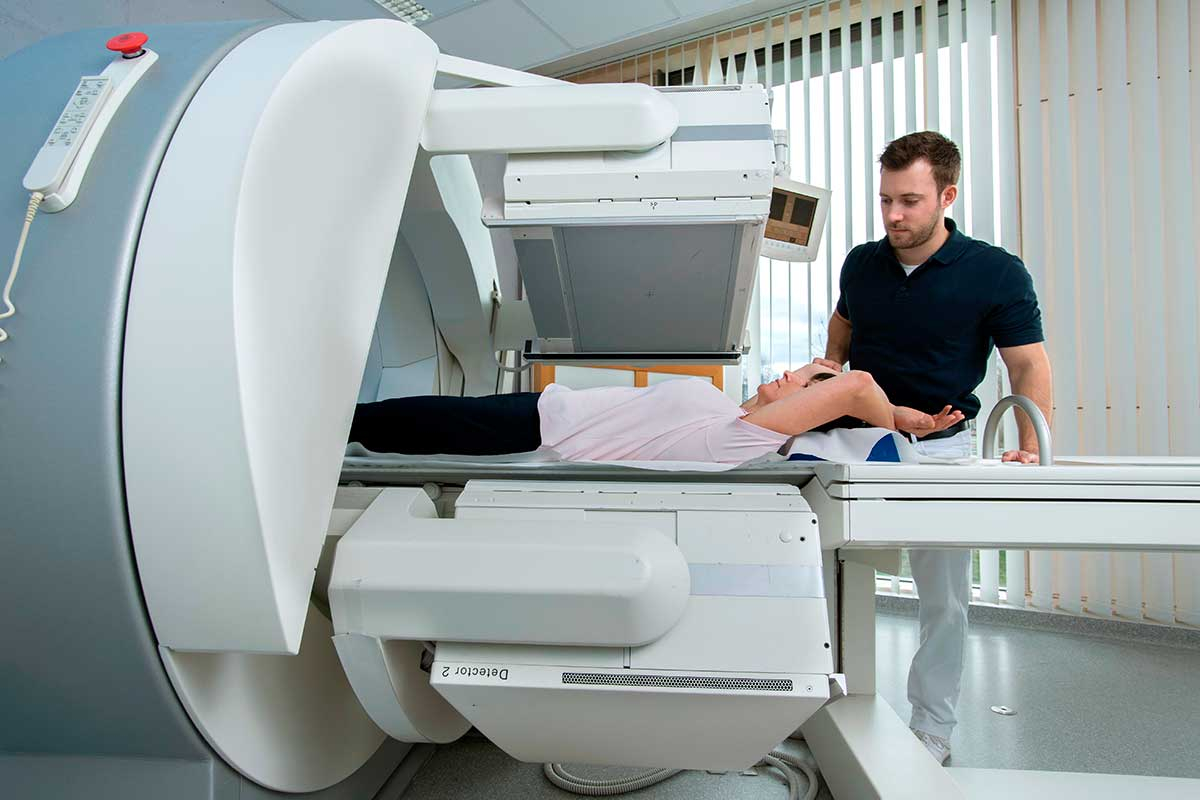
Scintigraphy
Scintigraphy is an imaging diagnostic test that uses small amounts of radioactive substances to evaluate the functioning of organs and structures within the body. This procedure, part of nuclear medicine, is widely used for its ability to detect physiological and metabolic changes before they become visible in other imaging tests like X-rays or CT scans.
The test is considered safe and effective, as it uses minimal amounts of radioactive material, which is quickly eliminated from the body. Its precision allows doctors to gather detailed information about the internal workings of the body, aiding in early diagnosis and monitoring of various health conditions.
What is Scintigraphy For?
Scintigraphy is used to diagnose, monitor, and follow up on a wide range of medical conditions, especially those related to organ function. For instance, it is widely employed to evaluate cardiac health, identify thyroid issues, detect hidden fractures, or locate tumors.
Beyond diagnosis, scintigraphy plays a crucial role in treatment planning and monitoring. It enables physicians to observe how the body responds to specific therapies, such as chemotherapy or radiation, and adjust approaches as needed to achieve the best outcomes.
How Does Scintigraphy Work?
Scintigraphy involves the use of a radioactive substance known as a radiopharmaceutical, which is administered to the patient through injection, ingestion, or inhalation, depending on the area being examined. This material emits radiation that is captured by a special device called a gamma camera, which produces detailed images of the area under study.
The procedure can last anywhere from 30 minutes to several hours, depending on the type of test and the organ being evaluated. During the test, the patient must remain still to ensure high-quality images. After the test, the radiopharmaceutical is naturally eliminated from the body, typically within 24 to 48 hours.
Types of Scintigraphy
1. Cardiac Scintigraphy
Used to assess blood flow and heart health. It is particularly useful in detecting coronary artery disease and analyzing heart muscle function after a heart attack.
2. Thyroid Scintigraphy
Focused on diagnosing conditions such as hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, or the presence of nodules. It provides detailed insights into thyroid function and structure.
3. Bone Scintigraphy
Indicated for detecting hidden fractures, bone infections, or metastatic cancer. It is one of the most common tests in nuclear medicine.
4. Renal Scintigraphy
Used to evaluate kidney function and diagnose conditions such as obstructions or renal insufficiency. It can also monitor kidney transplants.
5. Pulmonary Scintigraphy
Recommended for investigating pulmonary embolisms or evaluating respiratory function in chronic diseases.
What Conditions Can Scintigraphy Detect?
- Coronary Artery Disease: Identifies blockages in the heart's blood supply.
- Hyperthyroidism and Hypothyroidism: Assesses thyroid gland function.
- Hidden Fractures: Detects fractures not visible on standard X-rays.
- Bone Cancer and Metastases: Locates tumors and their spread to bones.
- Pulmonary Embolism: Diagnoses blood flow blockages in the lungs.
- Renal Insufficiency: Evaluates kidney problems and obstructions.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Detects inflammation in joints or other tissues.
When is Scintigraphy Recommended?
- Assessment of cardiac blood flow: For patients with suspected angina or heart attacks.
- Thyroid monitoring: In cases of previously detected dysfunction or nodules.
- Metastasis detection: For patients with a history of cancer.
- Identification of pulmonary embolism: In patients with shortness of breath or chest pain.
- Detection of hidden fractures: Especially in cases of osteoporosis or trauma.
- Renal function monitoring: Before or after a kidney transplant.
- Unexplained bone pain: To diagnose inflammation or infections.
Pre- and Post-Test Care for Scintigraphy
Pre-Test Care: Before the test, the patient should inform the doctor about any allergies, medications, and medical history. Depending on the type of scintigraphy, fasting or temporary discontinuation of certain medications may be required.
Post-Test Care: After the test, it is recommended to drink plenty of water to help eliminate the radiopharmaceutical from the body. Patients can resume normal activities unless otherwise instructed by their physician.
Contraindications for Scintigraphy
While safe for most patients, scintigraphy may be contraindicated in the following cases:
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women, due to exposure to radioactive material.
- Patients with known allergies to the radiopharmaceutical used.
- Individuals who cannot remain still during the examination.
Alternatives for Those Unable to Undergo Scintigraphy
- Ultrasound: A non-invasive alternative for evaluating certain organs.
- CT Scan: Ideal for detailed structural diagnoses.
- MRI: Suitable for analysis without radiation exposure.
Scintigraphy is available at Clinic Consultation. Book your test with us today and receive precise diagnostics with safety and quality. Contact us now!
Click the button below to schedule your appointment online.