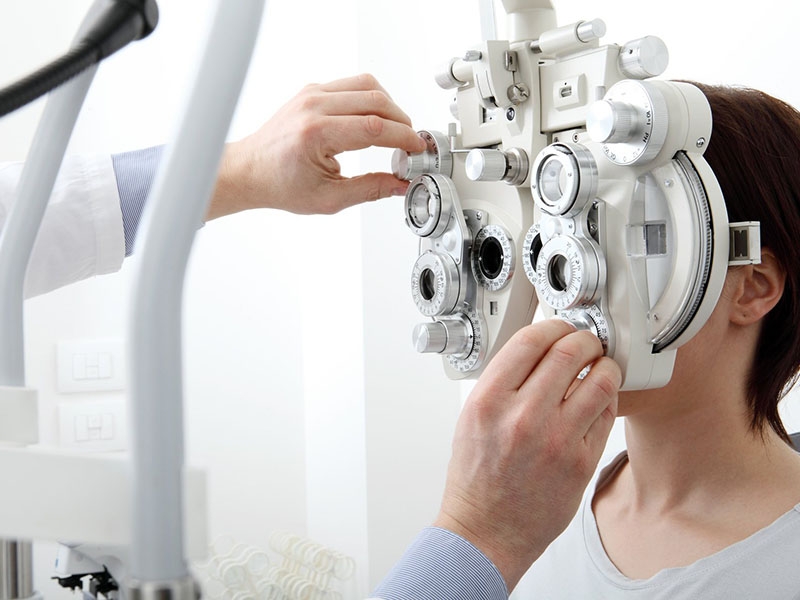
Ophthalmological Examination
An Ophthalmological Examination is a comprehensive eye exam conducted to evaluate the health of the eyes and assess vision clarity. It helps detect early signs of eye diseases, refractive errors (such as myopia or hyperopia), and other conditions that may affect vision. Eye exams are essential not only for maintaining optimal eye health but also for identifying potential systemic health issues like diabetes and hypertension, which can manifest in the eyes.
During the exam, an Ophthalmologist uses various tests and instruments to examine different parts of the eye, including the retina, optic nerve, cornea, and eye muscles. The goal is to ensure clear vision and diagnose any eye conditions early, which can prevent more serious problems from developing.
Types of Ophthalmological Examinations
Visual Acuity Test
A Visual Acuity Test is the most common part of an eye exam and is used to measure the clarity or sharpness of your vision. The patient is asked to read letters or symbols from a chart (Snellen chart) positioned at a distance. This test determines whether the patient has nearsightedness (myopia), farsightedness (hyperopia), or astigmatism, which may require corrective lenses or other treatments.
This test is quick and non-invasive, typically lasting only a few minutes. If the visual acuity test reveals vision problems, the ophthalmologist may prescribe glasses or contact lenses to correct the refractive error. Routine visual acuity tests are important for maintaining good vision and ensuring that corrective prescriptions are up to date.
Dilated Eye Exam
A Dilated Eye Exam is a more thorough procedure that allows the ophthalmologist to examine the back of the eye, including the retina, optic nerve, and blood vessels. The doctor uses eye drops to dilate (widen) the pupil, providing a better view of these internal structures. This test is essential for detecting conditions like glaucoma, macular degeneration, and diabetic retinopathy.
The dilated eye exam may take longer than other tests, as it requires about 20 to 30 minutes for the eye drops to fully dilate the pupils. After the exam, patients may experience light sensitivity and blurred vision for a few hours, so wearing sunglasses and arranging for someone else to drive may be necessary. Despite the temporary discomfort, this test is critical for diagnosing serious eye diseases early, helping to preserve vision.
Advantages of an Ophthalmological Examination
Ophthalmological exams offer several important benefits:
- Early detection of eye diseases: Comprehensive eye exams can detect early signs of serious eye conditions like glaucoma, cataracts, and retinal disorders, allowing for prompt treatment to prevent vision loss.
- Correction of vision problems: Routine exams help ensure that vision problems like nearsightedness, farsightedness, or astigmatism are identified and corrected with glasses or contact lenses.
- Overall health monitoring: Eye exams can also reveal signs of systemic conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol, as changes in the eye's blood vessels can indicate these problems.
The procedure itself is generally quick, with most exams lasting 30 to 60 minutes depending on the tests required. Regular eye exams are essential for maintaining long-term vision health.
Pre- and Post-exam Care
Pre-exam care: No special preparation is typically needed for a standard eye exam. However, if a dilated eye exam is planned, patients should avoid driving afterward due to the temporary blurring and light sensitivity. It’s helpful to bring sunglasses and ensure you have someone available to drive you home if necessary.
Post-exam care: After a dilated eye exam, patients may experience sensitivity to light and blurred vision for a few hours. It’s important to wear sunglasses to protect your eyes from bright lights and to avoid tasks requiring clear vision, such as reading or using digital screens, until your vision returns to normal.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How often should I get an eye exam?
It is recommended to have an eye exam every 1 to 2 years, especially for adults over 40 or individuals with a history of eye problems. Those with specific conditions like diabetes may need more frequent exams.
2. Does the dilated eye exam hurt?
No, the dilated eye exam is painless. You may experience mild discomfort from light sensitivity, but this is temporary and subsides after a few hours.
3. Can eye exams detect health problems?
Yes, eye exams can reveal signs of other health conditions, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol, by examining the blood vessels in the eye.
Ophthalmological Examination Services at Clinic Consultation
At Clinic Consultation, we offer comprehensive ophthalmological exams to ensure your eyes are healthy and your vision is clear. Whether you're experiencing vision problems or need a routine check-up, our experienced ophthalmologists provide personalized care using the latest diagnostic tools.
Book an appointment today to schedule your eye exam at Clinic Consultation and take the first step toward better eye health.
Click the button below to schedule your appointment online.